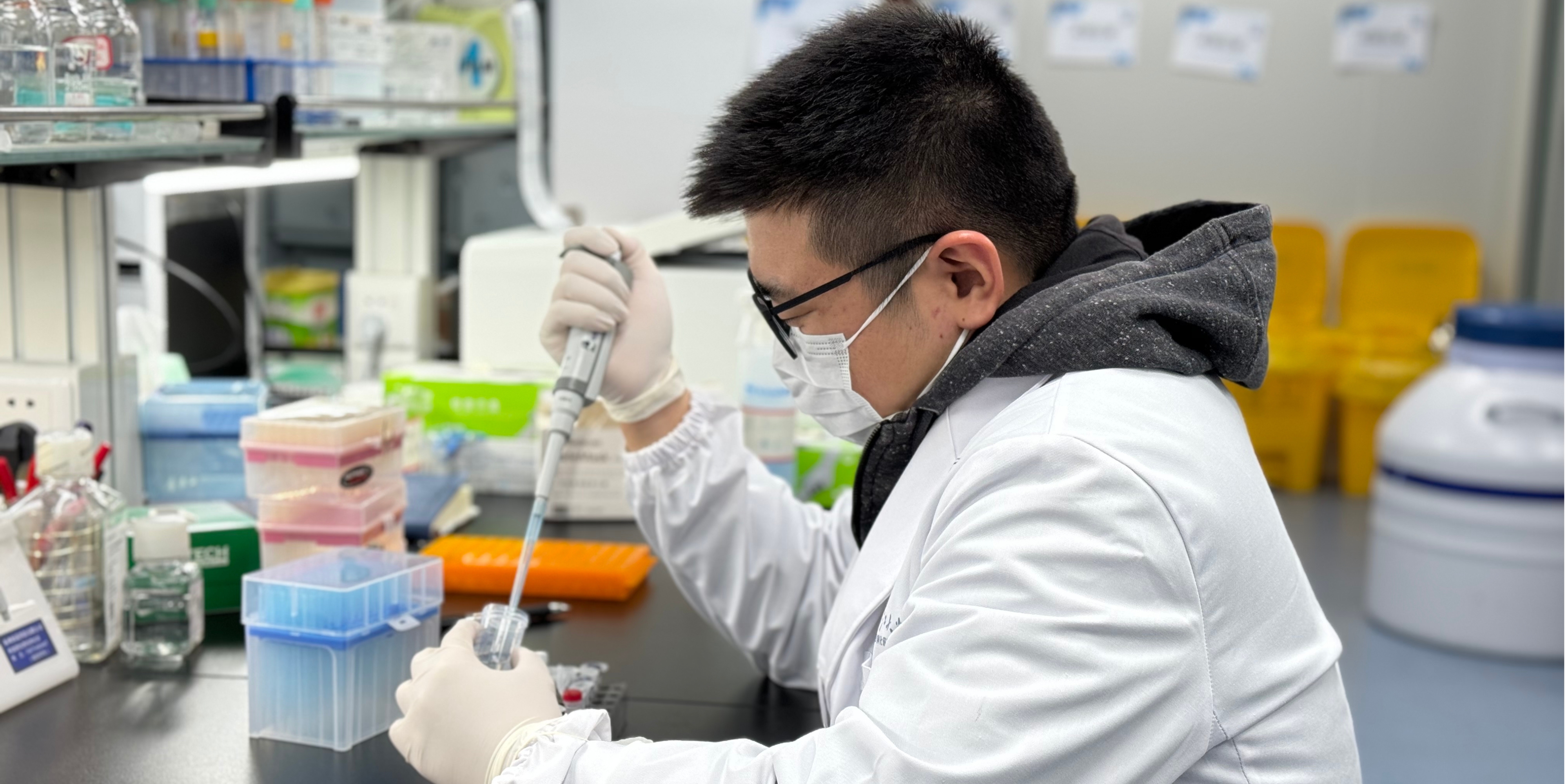
Our research encompasses broad topics in evolution, ranging from the micro-level exploration of evolutionary mechanisms and developmental regulation to the macro-scale examination of evolutionary patterns across life kingdom.
Our study encompasses a diverse array of species and wide spectrum of phenotypes. We aim to provide organism level understanding on the emergence of new traits and the new species by integrating interdisciplinary data and tools under the framework of evolutionary theory.

OUR RESEARCH
-
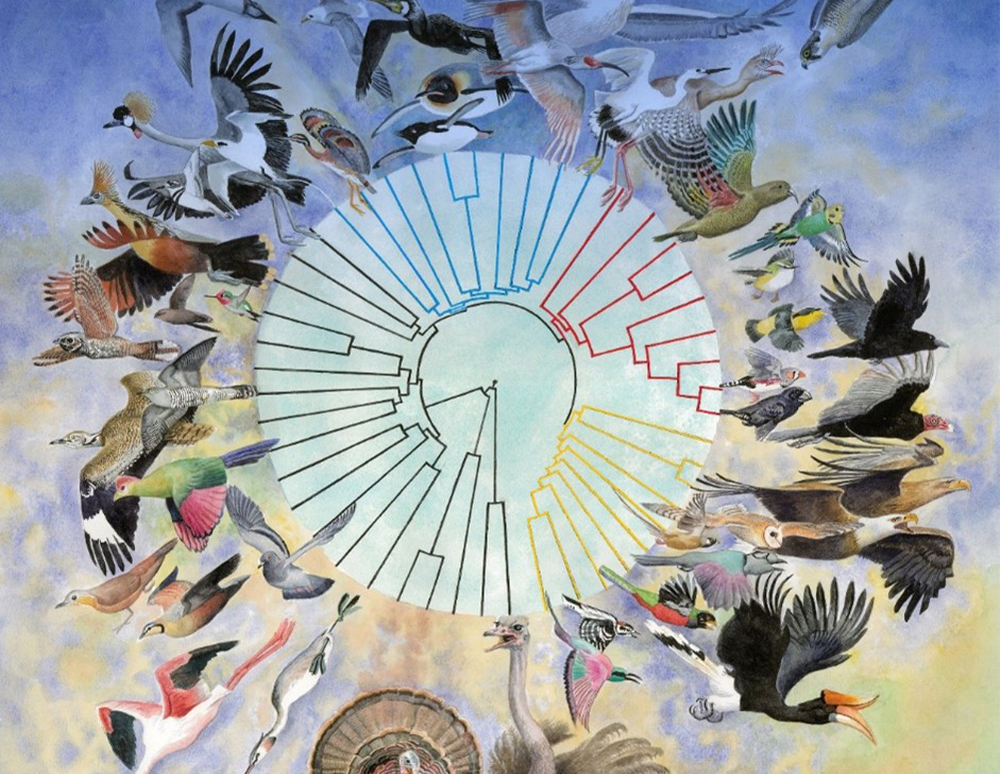

The phylogeny is fundamental for our understanding of biodiversity, and allows biologists to address questions in a wide variety of fields, such as taxonomy, molecular evolution, population genetics, and developmental biology. Our center focus on developing and applying technologies to infer the “Net of Life” from the whole genome data of a large number of species, and to clarify the multiple sources of heterogeneity in phylogenetic signals across genomic loci. The achievement of that mission will provide the insights in explanation of origin and adaptive evolution of species on earth.
Phylogenomics and biodiversity
The phylogeny is fundamental for our understanding of biodiversity, and allows biologists to address questions in a wide variety of fields, such as taxonomy, molecular evolution, population genetics, and developmental biology. Our center focus on developing and applying technologies to infer the “Net of Life” from the whole genome data of a large number of species, and to clarify the multiple sources of heterogeneity in phylogenetic signals across genomic loci. The achievement of that mission will provide the insights in explanation of origin and adaptive evolution of species on earth.
-
A small number of extraordinary evolutionary transitions have profound impacts in establishing the modern biodiversity. These transitions often involve the emergency of novel life forms and new way of storage and transmission of information, contributing the increase of evolutionary complexity. We are interested in genomic basis underlying some of these key transitions, such as evolution of sex, origin of superorganism, and human society.
Genomic evolution of major transition
A small number of extraordinary evolutionary transitions have profound impacts in establishing the modern biodiversity. These transitions often involve the emergency of novel life forms and new way of storage and transmission of information, contributing the increase of evolutionary complexity. We are interested in genomic basis underlying some of these key transitions, such as evolution of sex, origin of superorganism, and human society.
-
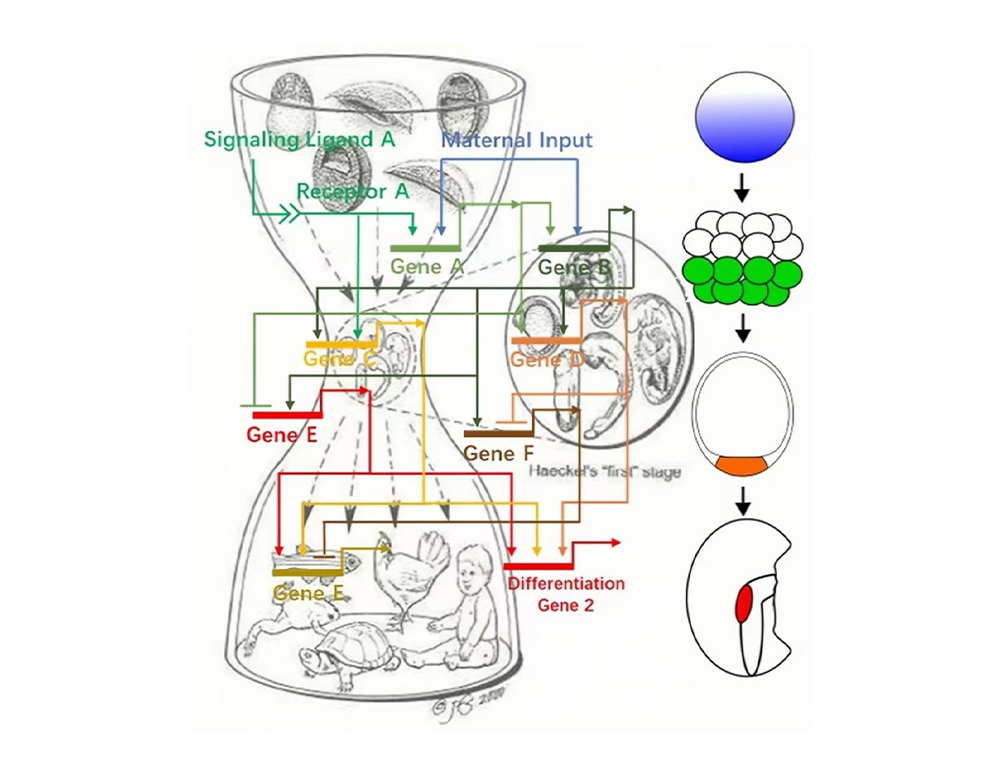
A key to understand animal evolution is by studying the evolutionary and molecular mechanisms of traits adapted to respective niches. Given each trait is likely sculped by a combination of genetic and environmental factors during developmental process, we are to precisely determine where, when and how a trait is determined by cutting-edge omic methods, and provide retrospective insights into general processes of evo-devo.
Marcoevolutionary developmental biology
A key to understand animal evolution is by studying the evolutionary and molecular mechanisms of traits adapted to respective niches. Given each trait is likely sculped by a combination of genetic and environmental factors during developmental process, we are to precisely determine where, when and how a trait is determined by cutting-edge omic methods, and provide retrospective insights into general processes of evo-devo.
-

Evolutionary medicine or Darwinian medicine is the application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease. Natural selection leaves footprints in the genome and has significant impact in shaping our genomic structure, including the genetic components causing diseases.
We study the DNA record to gain insight into the patterns and processes of human health and disease across animals, focusing on two major questions:
1) What are the evolutionary constrains of human aging?
2)What factors leave us susceptible to disease?
Evolutionary implication on medicine
Evolutionary medicine or Darwinian medicine is the application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease. Natural selection leaves footprints in the genome and has significant impact in shaping our genomic structure, including the genetic components causing diseases.
We study the DNA record to gain insight into the patterns and processes of human health and disease across animals, focusing on two major questions:
1) What are the evolutionary constrains of human aging?
2)What factors leave us susceptible to disease?
-
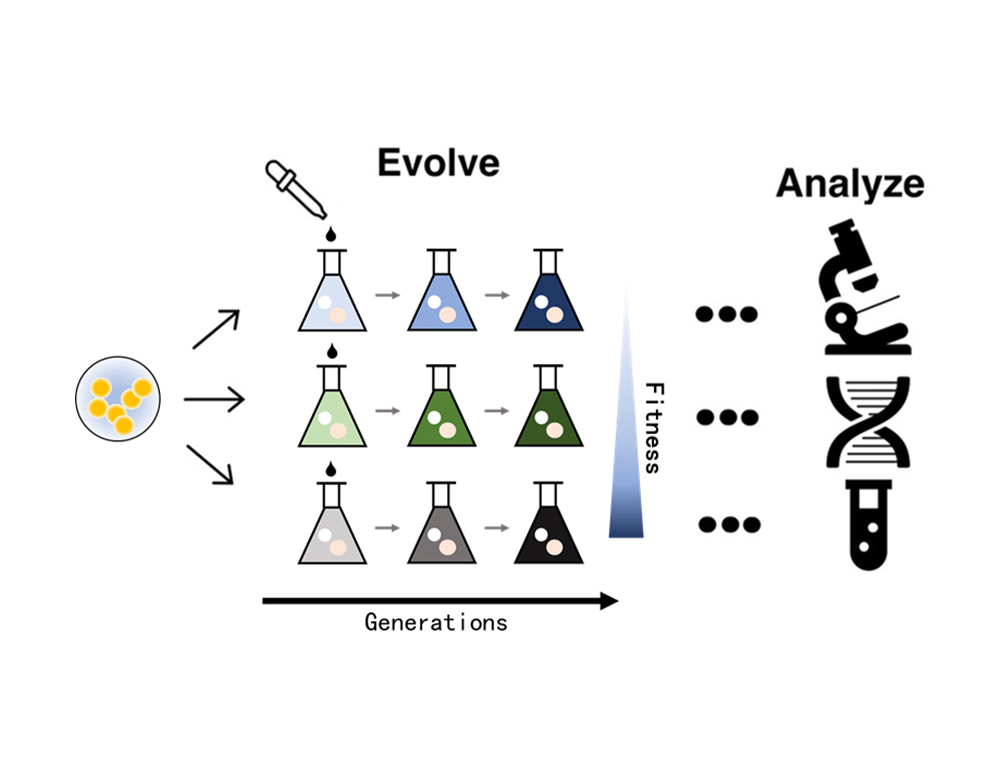
Experimental evolution is a scientific approach in which controlled selection pressures are applied to populations of living organisms , such as E. coli and yeast, in laboratory environment. This approach allows us to observe and study the process of evolution in real time and has been particularly useful in understanding the fundamental principles of evolutionary biology and addressing specific questions about adaptation, genetic variation, and evolutionary mechanisms.
Experimental evolution
Experimental evolution is a scientific approach in which controlled selection pressures are applied to populations of living organisms , such as E. coli and yeast, in laboratory environment. This approach allows us to observe and study the process of evolution in real time and has been particularly useful in understanding the fundamental principles of evolutionary biology and addressing specific questions about adaptation, genetic variation, and evolutionary mechanisms.